Contributions
- We have demonstrated how brain T2 values change with time postmortem.
- We have shown that T2 constants measured ex-vivo are linearly related to T2 constants measured in-vivo.
- We have established that hippocampal volume measured ex-vivo is related to multiple cognitive abilities assessed proximate to death, with its strongest association with episodic memory.
- We have demonstrated that regional brain volumes remain relatively unchanged across time postmortem, at least for the first 6 months after death.
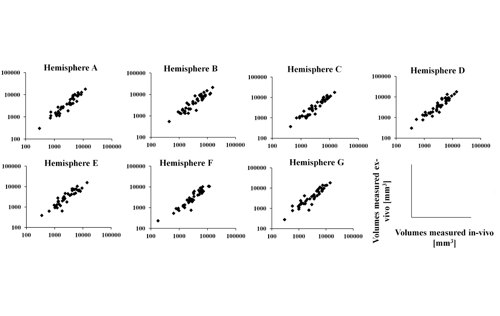
- We have found a close linear correspondence between in-vivo and ex-vivo regional brain volume measurements.
- We have shown that ex-vivo magnetic susceptibility does not change systematically over time postmortem, and that, gray matter susceptibility measured ex-vivo may be well modeled as a linear function of susceptibility measured in-vivo.
- We have demonstrated that ex-vivo diffusion anisotropy is linearly related to diffusion anisotropy measured in-vivo.
- We have shown that white matter hyperintensities (WMH) burden is the same in-vivo and ex-vivo for short antemortem intervals, and higher ex-vivo than in-vivo for higher antemortem intervals.
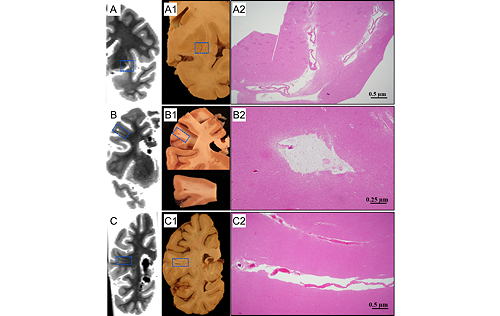
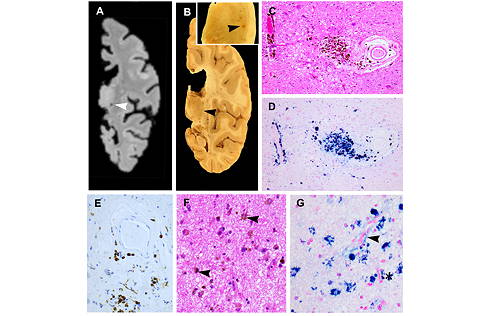
- We have histologically confirmed cerebral microbleeds detected ex-vivo.
- We have histologically confirmed enlarged perivascular spaces detected ex-vivo.
Ex-vivo MRI provides images at essentially the same time as histological examination of the tissue, and, therefore, allows linking MRI signals to neuropathology findings. Although long scan times are feasible in ex-vivo MRI (generating higher spatial resolution and/or signal to noise ratio compared to in-vivo imaging), we have chosen to collect ex-vivo MRI data with in-vivo-like image properties to facilitate translation. Using this approach, we have developed a unique large database including longitudinal clinical, in-vivo MRI, ex-vivo MRI and neuropathology data on the same persons, and have demonstrated how to perform translational ex-vivo brain MRI.
Selected Related Publications
- Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Vasireddi SK, Arfanakis K. Postmortem MRI of human brain hemispheres: T2 relaxation times during formaldehyde fixation. Magn Reson Med 2009;61:810-818.
- Dawe RJ, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Arfanakis K. Neuropathologic correlates of hippocampal atrophy in the elderly: a clinical, pathologic, postmortem MRI study. PLoS One 2011;6:e26286.
- Kotrotsou A, Bennett DA, Schneider JA, Dawe RJ, Golak T, Leurgans SE, Yu L, Arfanakis K. Ex vivo MR volumetry of human brain hemispheres. Magn Reson Med 2014;71:364-374.
- Evia AM, Kotrotsou A, Tamhane AA, Dawe RJ, Kapasi A, Leurgans SE, Schneider JA, Bennett DA, Arfanakis K. Ex-vivo quantitative susceptibility mapping of human brain hemispheres. PLoS One 2017;12:e0188395.
- Arfanakis K, Evia AM, Leurgans SE, Cardoso LFC, Kulkarni A, Alqam N, Lopes LF, Vieira D, Bennett DA, Schneider JA. Neuropathologic Correlates of White Matter Hyperintensities in a Community-Based Cohort of Older Adults. J Alzheimers Dis 2020;73:333-345.
- Javierre-Petit C, Schneider JA, Kapasi A, Makkinejad N, Tamhane AA, Leurgans SE, Mehta RI, Barnes LL, Bennett DA, Arfanakis K. Neuropathologic and Cognitive Correlates of Enlarged Perivascular Spaces in a Community-Based Cohort of Older Adults. Stroke 2020;51:2825-2833.
- Nag S, Chen EY, Johnson R, Tamhane A, Arfanakis K, Schneider JA. Ex vivo MRI facilitates localization of cerebral microbleeds of different ages during neuropathology assessment. Free Neuropathol 2021;2:35.